Electrical Safety Day is observed every year across India to raise awareness about the risks associated with electricity and promote best practices for electrical safety in homes, workplaces and public spaces. Introduced by the Central Electricity Authority (CEA) under the Ministry of Power, Government of India, this observance is supported by various state electricity boards, utilities, industries and safety organizations. The day serves as a critical reminder that while electricity is essential to modern life, it must be managed with care, expertise and strict safety standards.
In recent years, the need for electrical safety has become even more urgent. As India undergoes a rapid transformation in its energy sector, the widespread adoption of clean and smart technologies presents both opportunities and new safety challenges. Electrical Safety Day 2025, held on June 26, embraces this evolution with the theme “Smart Energy Safe Nation.” This theme reflects the growing intersection between sustainability, technology and safety, calling attention to the importance of integrating safety protocols into every stage of our clean energy journey.
What is Electrical Safety Day?
Electrical Safety Day is an annual observance dedicated to promoting awareness about the safe use of electricity and the importance of preventing electrical hazards. It is traditionally aligned with National Electrical Safety Month and is actively supported by a wide range of stakeholders, including regulatory bodies, utility companies, electrical equipment manufacturers, training institutions and nonprofit organizations.

Its goal is to reduce the number of electrical accidents, which continue to be a leading cause of workplace injuries, residential fires and fatalities around the world. Activities on this day may include awareness campaigns, safety audits, public workshops, safety pledge drives and training sessions aimed at improving knowledge and behavior related to electrical safety.
Electrical Safety Day 2025 Theme
The official theme for Electrical Safety Day 2025, announced by the Central Electricity Authority (CEA) of India, is “Smart Energy Safe Nation.” This theme reflects a vital message for the modern era: as countries embrace cleaner and smarter energy technologies, the focus on electrical safety must become stronger and more comprehensive.
New energy systems are reshaping the way we generate, store and consume electricity. Technologies such as Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS), Electric Vehicle Charging Systems (EVCS) and Rooftop Solar Installations are central to achieving sustainability goals. However, with these advancements come new types of electrical hazards. These are no longer limited to traditional wiring faults or overloads. Instead, we now face challenges that require advanced knowledge, professional handling and continuous safety oversight.
Key Areas of Concern in the Smart Energy Landscape
As India and many other nations move rapidly toward cleaner and smarter energy systems, the complexity of electrical infrastructure is increasing. Technologies like Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS), Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure (EVCI) and Rooftop Solar Photovoltaics (PV) are transforming the way electricity is produced, stored and consumed. However, with this progress come several critical areas of concern that must be addressed to ensure safety, reliability and long-term sustainability.

Battery Energy Storage Systems
Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) are becoming essential for managing energy demand and stabilizing the grid. They store electricity generated from renewable sources for use during peak hours or outages. Despite their benefits, BESS units present serious safety risks. Improper installation, lack of thermal management or internal faults can lead to overheating, toxic gas release or in extreme cases, fire and explosion. These systems require strict adherence to safety protocols, proper enclosure, ventilation and monitoring technologies.
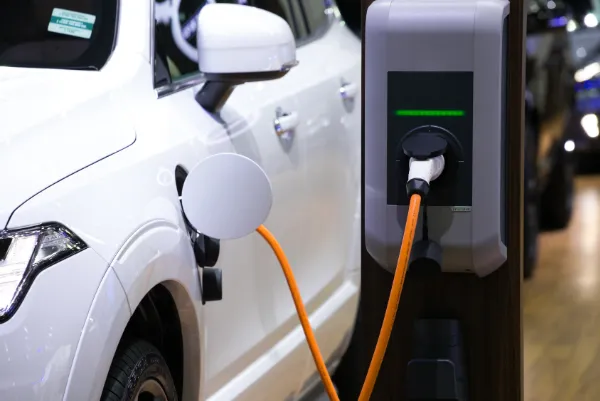

Electric Vehicle Charging Systems
Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure (EVCI) is expanding rapidly in both residential and public spaces. High-voltage equipment, constant plugging and unplugging and outdoor exposure create multiple hazards. Common risks include electric shock, overheating connectors, short circuits due to water ingress and mechanical wear on cables. Ensuring that EV chargers are installed according to proper electrical codes, equipped with earth fault protection and regularly maintained is essential for user safety.
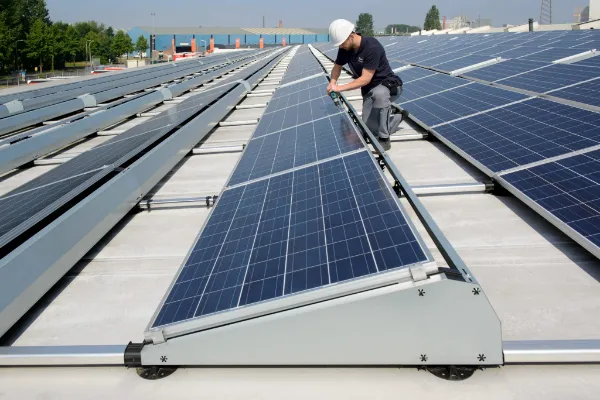

Rooftop Solar Systems
Rooftop Solar Systems are one of the most accessible and scalable clean energy solutions. However, they often involve live DC wiring on rooftops, which can remain energized even when the grid is shut down. This creates a risk of electric shock, especially during maintenance or emergencies. Improper system design, inadequate earthing and lack of surge protection can also lead to equipment failure or fire. Using certified components, hiring trained professionals and performing periodic inspections are key preventive measures.
The smart energy landscape also demands attention to integration and interoperability. When multiple systems like solar panels, batteries and EV chargers operate together, their combined electrical behavior must be properly coordinated. Poor integration can result in load imbalances, reverse current and dangerous fault conditions.
Common Electrical Hazards in Modern Installations
As modern energy systems such as rooftop solar, battery storage and electric vehicle charging become more widespread, the types of electrical hazards have also evolved. These hazards are not limited to traditional wiring faults but now extend to issues specific to high-voltage systems, direct current (DC) applications and complex power electronics. Understanding these risks is essential for both users and professionals involved in planning, installing and maintaining electrical systems.

1. Overload and Overcurrent
This occurs when electrical circuits are exposed to more current than they are designed to handle. The result is overheating of cables, switchboards or distribution panels, which can lead to insulation breakdown, fire or even equipment failure. It is commonly caused by improper load calculation or the use of undersized conductors.
2. DC Arcing
Direct current (DC) systems are more likely to produce sustained electric arcs than alternating current (AC) systems. Even at low current levels, a DC arc can generate intense heat and potentially ignite nearby materials. DC arcing is a particular concern in solar panels, battery storage units and inverter connections.
3. Reverse Current or Backfeed
This happens when power flows in the opposite direction from what the system was designed for, such as during grid outages when rooftop solar panels continue supplying electricity. Without isolation mechanisms, this can damage appliances and pose a serious risk to maintenance personnel or utility workers.
4. Thermal Instability
Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) are sensitive to temperature variations. Internal short circuits, cell degradation or poor ventilation can lead to overheating, thermal runaway or in severe cases, fire and explosion. This hazard is particularly critical when lithium-ion batteries are used.
5. Electric Shock
Electric shocks can result from exposed live parts, damaged insulation, wet conditions or faulty grounding. Common sources include EV charging stations and rooftop solar installations. Poor weather protection or user mishandling can further increase the risk.
6. Lightning and Voltage Surges
Voltage spikes caused by lightning strikes or power fluctuations can destroy sensitive electronic components in smart meters, inverters or control units. Rooftop systems are especially vulnerable due to their elevated, open-air positioning.
7. Poor Installation and Maintenance
Improper installation is one of the leading causes of electrical accidents in modern systems. Loose connections, use of substandard materials, poor-quality workmanship and a lack of routine inspections can lead to overheating, arcing or fire. Every modern energy system, regardless of size, is susceptible to these risks if not properly maintained.
Electrical Safety Day 2025
Best Practices for Ensuring Electrical Safety in Smart Energy Systems
As smart energy technologies such as battery storage, electric vehicle charging and rooftop solar become more common, ensuring electrical safety is more important than ever. These systems often operate at higher voltages, involve complex components and require careful planning, installation and maintenance. Adopting a safety-first approach is essential to prevent accidents, system failures and long-term hazards.

Here are key best practices to follow across the lifecycle of smart energy systems:
1. Comply with Relevant Standards and Codes
All installations should meet national and international safety standards. For example:
• IS 16221–1 for Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS)
• IS/IEC 61851 for Electric Vehicle Charging Equipment
• IEC 60364 for Low Voltage Electrical Installations
Adherence to these standards ensures that systems are designed and tested for safety, reliability and durability.
2. Use Certified and High-Quality Components
Avoid low-quality or counterfeit equipment. Always choose components that are certified by recognized testing bodies such as BIS, IEC or UL. This applies to batteries, solar panels, inverters, cables, connectors and protective devices.
3. Ensure Proper System Design
System design should consider load calculations, fault currents, surge protection and earthing. Coordination between components is essential to avoid overload, backfeed and instability. In hybrid systems, integration between solar, battery and grid supply must be carefully planned.
4. Hire Qualified Professionals for Installation
Only trained and certified electricians or technicians should install smart energy systems. Improper installation remains one of the leading causes of electrical accidents. Qualified professionals understand layout planning, proper wiring techniques and required clearances.
5. Incorporate Safety Devices and Monitoring Systems
• Smart energy systems should include safety features such as:
• Residual Current Devices (RCDs)
• Surge Protection Devices (SPDs)
• Battery Management Systems (BMS)
• Overload protection and fuses
Advanced systems may also use smart monitoring tools to track system health, voltage levels and detect faults in real time.
6. Conduct Routine Inspection and Maintenance
Periodic inspections help identify early signs of wear, corrosion, insulation damage or loose connections. Maintenance schedules should include:
• Thermal imaging to detect hotspots
• Battery health analysis
• Visual inspections for water ingress or mechanical damage
• Software updates for energy management systems
7. Provide User Awareness and Training
Users and maintenance staff should receive basic training on the risks associated with EV chargers, batteries and rooftop solar systems. Training should cover emergency procedures, system shutdown protocols and how to recognize warning signs.
8. Implement Fire Safety and Emergency Preparedness
Install fire extinguishers suitable for electrical fires near high-risk areas. Develop emergency response plans, especially in commercial or multi-user installations. Ensure proper ventilation in enclosed battery storage areas to prevent overheating.
Conclusion
Electrical Safety Day 2025 reinforces a vital message: as we move toward smarter and cleaner energy systems, safety must be an essential part of the journey. The theme “Smart Energy Safe Nation” highlights the need to embed safety practices into every phase of our energy transition, from system design and equipment selection to installation, usage and maintenance.
This is a collective responsibility. Government agencies must enforce regulations, industries must follow quality standards, professionals must be properly trained and users must stay informed. Each stakeholder has a role in building a safer energy future.
When safety becomes a shared value, progress becomes more meaningful. By working together, we can ensure that the benefits of modern energy technologies are realized without compromising the well-being of people, property or the environment.